The Homunculus & Sensory-Motor Feedback: Applications in Soft-Tissue, Acupuncture, Stretching, & Chiropractic Care
The human brain is a marvel of intricate design, with specialized regions responsible for various functions. One of the most fascinating concepts in neuroscience is the "homunculus," a visual representation of the sensory and motor regions of the brain. Understanding the homunculus and the mechanisms of sensory-motor feedback provides critical insights into how our bodies interact with the world.
The Homunculus: A Map of Sensory and Motor Functions
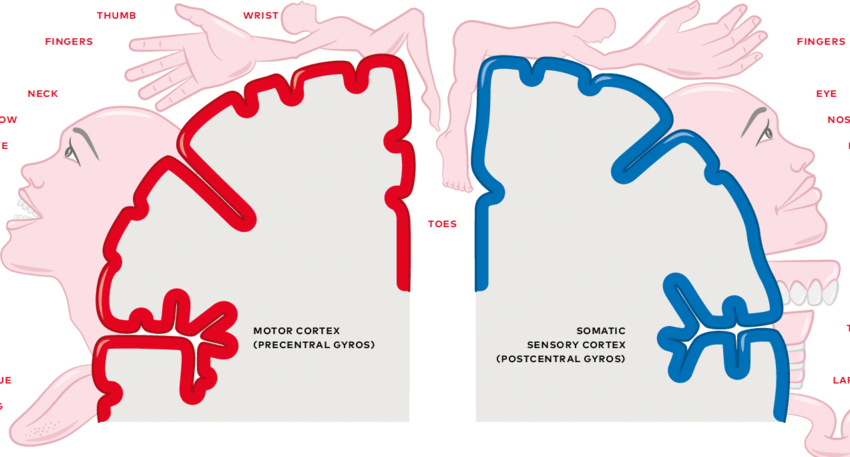
The homunculus, often depicted as a distorted human figure, represents the brain's somatosensory and motor cortex. It illustrates how different body parts are mapped onto these cortical areas.
Sensory Homunculus
The sensory homunculus is located in the primary somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus) and illustrates the sensory distribution across the body. This map is based on the density of sensory receptors in various body parts. For example, the lips, hands, and face are disproportionately larger than other body parts because they have a higher density of sensory receptors, thus requiring more cortical space (Penfield & Boldrey, 1937).
Motor Homunculus
The motor homunculus is found in the primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus) and represents the distribution of motor control across different body parts. Like the sensory homunculus, body parts with finer motor control, such as the hands and face, occupy more cortical space (Penfield & Rasmussen, 1950).
Sensory-Motor Feedback Mechanisms
Sensory-motor feedback is how sensory information is used to guide motor actions. This feedback loop is crucial for precise and coordinated movements. Sensory receptors in the skin, muscles, and joints send information about the body's position and movement to the brain. The brain then processes this information and sends signals to the muscles to adjust their activity.
Proprioception
Proprioception, often called the "sixth sense," is the body's ability to perceive its position in space. Proprioceptive feedback is essential for tasks that require balance and coordination. Research shows that proprioceptive information is integrated with the somatosensory cortex and used by the motor cortex to fine-tune movements (Proske & Gandevia, 2012).
Motor Learning
Motor learning involves improving motor skills through practice and experience. Sensory feedback plays a critical role in motor learning by allowing the brain to make corrections based on errors detected during movement. Studies have shown that effective motor learning depends on sensory pathways' integrity and interaction with motor pathways (Wolpert et al., 2011).
Clinical Implications
Understanding the homunculus and sensory-motor feedback mechanisms has significant implications for various therapeutic practices, including soft tissue therapy, acupuncture, stretching, and chiropractic care.
Soft Tissue Therapy
Soft tissue therapy can enhance proprioceptive feedback by stimulating sensory receptors in the skin and muscles. This stimulation can improve body awareness and motor control, which is particularly beneficial for individuals recovering from injuries (Field, 2014).
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a practice rooted in traditional Chinese medicine, has been shown to influence sensory-motor feedback by stimulating specific points on the body. Research suggests that acupuncture can modulate brain activity and enhance sensory-motor integration, improving motor function and relieving pain (Ahsin et al., 2009).
Stretching
Stretching exercises enhance flexibility and proprioception by increasing the range of motion and stimulating sensory receptors in the muscles and joints. Regular stretching can improve motor performance and reduce the risk of injuries (Behm et al., 2016).
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic adjustments aim to restore proper alignment and function of the musculoskeletal system. These adjustments can improve sensory-motor feedback by enhancing joint proprioception and reducing pain, thus facilitating better motor control (Haavik & Murphy, 2012).
Integration of Therapies
Integrating various therapeutic practices that target sensory-motor feedback can enhance overall patient outcomes. For example, combining soft tissue therapy, acupuncture, stretching, and chiropractic care can create a comprehensive approach to improving proprioception and motor control. Research indicates that such integrative approaches can more effectively manage chronic pain and enhance functional recovery (Hodges & Cholewicki, 2019).
Conclusion
The homunculus provides a valuable visual representation of how the brain allocates cortical space to different body parts based on sensory and motor functions. Sensory-motor feedback mechanisms are crucial for coordinated movement and motor learning. By understanding these concepts, various therapeutic practices can be developed and refined to enhance patient outcomes and promote recovery from neurological and musculoskeletal disorders.
References
- Ahsin, S., Saleem, S., Bhatti, A. M., Iles, R. K., Aslam, M., & Gillani, S. A. (2009). Clinical and physiological effects of acupuncture on asthma: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, 15(5), 607-616. https://doi.org/10.1089/acm.2008.0546
- Behm, D. G., Blazevich, A. J., Kay, A. D., & McHugh, M. (2016). Acute effects of muscle stretching on physical performance, range of motion, and injury incidence in healthy active individuals: a systematic review. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 41(1), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2015-0235
- Field, T. (2014). Massage therapy research review. Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice, 20(4), 224-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctcp.2014.07.002
- Haavik, H., & Murphy, B. (2012). The role of spinal manipulation in addressing disordered sensorimotor integration and altered motor control. Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology, 22(5), 768-776. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2012.02.012
- Hodges, P. W., & Cholewicki, J. (2019). Building a Collaborative Model of Therapeutic Interventions. In P. W. Hodges & J. Cholewicki (Eds.), The Relationship Between Pain, Movement, and Motor Control and the Implications for Injury Prevention and Rehabilitation (pp. 307-322). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-812162-7.00024-2
- Penfield, W., & Boldrey, E. (1937). Somatic motor and sensory representation in the cerebral cortex of man as studied by electrical stimulation. Brain, 60(4), 389-443. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/60.4.389
- Penfield, W., & Rasmussen, T. (1950). The cerebral cortex of man; a clinical study of localization of function. New York: Macmillan.
- Proske, U., & Gandevia, S. C. (2012). The proprioceptive senses: their roles in signaling body shape, body position and movement, and muscle force. Physiological Reviews, 92(4), 1651-1697. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00048.2011
- Taub, E., Uswatte, G., & Pidikiti, R. (1999). Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy: a new family of techniques with broad application to physical rehabilitation—a clinical review. Journal of Rehabilitation Research and Development, 36(3), 237-251.
- Wolpert, D. M., Diedrichsen, J., & Flanagan, J. R. (2011). Principles of sensorimotor learning. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 12(12), 739-751. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3112