Understanding Muscular Imbalances and Reciprocal Inhibition: Practical Applications for Mobility and Exercise
Muscular imbalances and reciprocal inhibition are critical concepts in exercise science and physical therapy that can significantly impact performance, injury prevention, and overall mobility. This blog explores these concepts, supported by recent research, and provides practical applications for integrating them into your mobility and exercise routines.
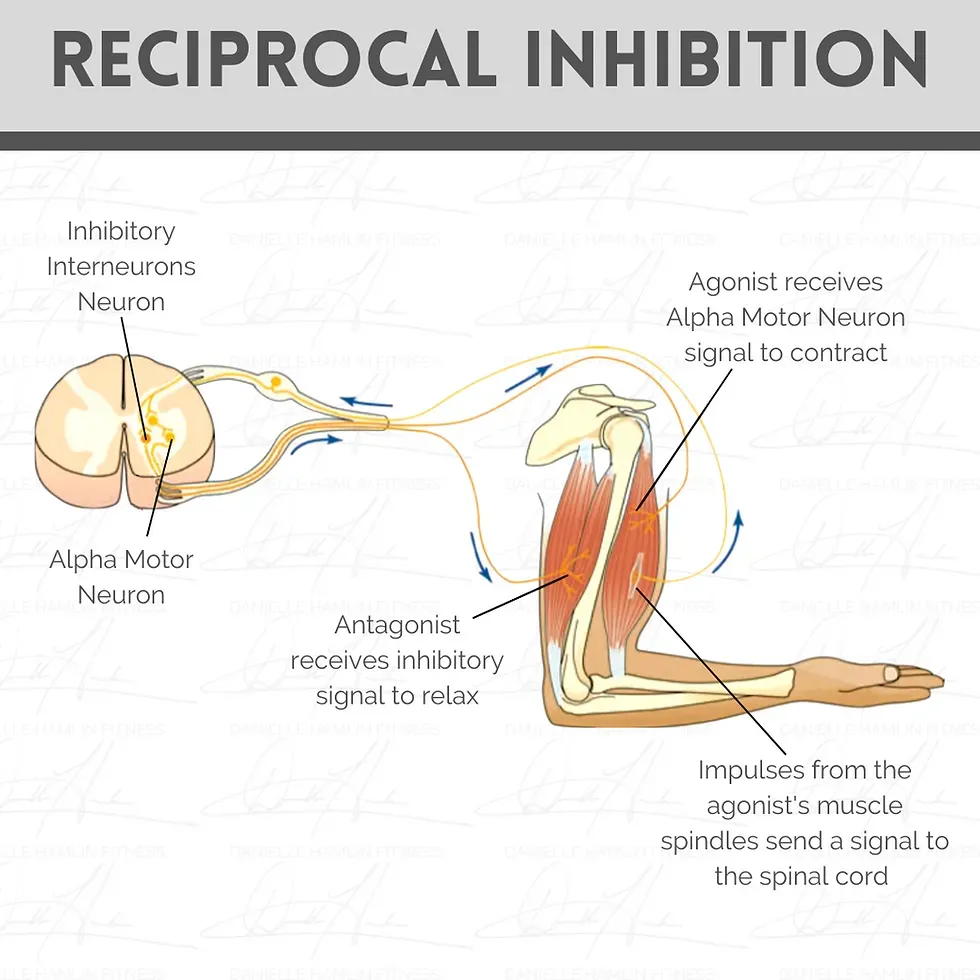
What Are Muscular Imbalances?
Muscular imbalances occur when there is a disparity in the strength or flexibility between opposing muscle groups. This can lead to improper movement patterns, decreased performance, and a higher risk of injuries. For example, if the quadriceps are significantly stronger than the hamstrings, this imbalance can increase the risk of knee injuries (American Council on Exercise, 2019).
Understanding Reciprocal Inhibition
Reciprocal inhibition is a neuromuscular phenomenon where the activation of one muscle group (the agonist) inhibits the activation of the opposing muscle group (the antagonist). This process is essential for smooth and coordinated movements. For instance, when you contract your biceps, reciprocal inhibition ensures that your triceps relax to allow the movement to occur efficiently (American Council on Exercise, 2019).
Recent Research Insights
Recent studies have emphasized the importance of addressing muscular imbalances and optimizing reciprocal inhibition for better mobility and injury prevention:
- Joint Mobility and Stability: Research from the American Council on Exercise highlights the significance of maintaining appropriate joint mobility and stability. Proper joint function ensures that stable joints provide the necessary support while mobile joints allow for a full range of motion. This balance helps prevent compensatory movements that can lead to imbalances and injuries (American Council on Exercise, 2019).
- Physical Activity and Posture: A systematic review in BMC Public Health found a complex relationship between physical activity and posture. The review suggests that regular physical activity can help maintain proper posture, which in turn can prevent musculoskeletal conditions related to imbalances (Fazli et al., 2023).
- Electromyography (EMG) Monitoring: Advances in EMG monitoring have provided deeper insights into muscle activation patterns. EMG can be used to assess and correct imbalances by identifying underactive muscles and ensuring that they are properly activated during exercises (Abu Owida et al., 2023).
- Reciprocal Inhibition Techniques: A recent study by Jawade et al. (2023) examined the effects of reciprocal inhibition techniques on pain, range of motion, and functional activities in patients with upper trapezitis. The study found significant improvements, suggesting that these techniques can be beneficial for managing muscular imbalances and improving functional outcomes (Jawade et al., 2023).
- Neural Mechanisms of Muscle Coordination: A study published in Frontiers in Neuroscience explored the neural mechanisms underlying muscle coordination and reciprocal inhibition. The researchers highlighted the importance of neural control in maintaining muscle balance and coordination, emphasizing the role of the central nervous system in managing muscular imbalances and optimizing movement patterns (Ritzmann et al., 2023).
Implementing These Concepts into Practice
To integrate the principles of muscular imbalances and reciprocal inhibition into your exercise and mobility routines, consider the following strategies:
- Comprehensive Assessments: Begin with a thorough assessment of your muscle strength and flexibility. Identify any imbalances between opposing muscle groups. Tools like EMG can offer precise data on muscle activation patterns.
- Balanced Training Programs: Design your training program to address identified imbalances. Incorporate exercises that strengthen weaker muscles and ensure that dominant muscles do not become overly tight or strong relative to their antagonists.
- Dynamic Stretching and Mobility Work: Incorporate dynamic stretching and mobility exercises into your warm-up routine. These exercises should focus on improving the range of motion in joints that require mobility while maintaining stability in others.
- Neuromuscular Training: Engage in neuromuscular training that emphasizes the coordination between agonist and antagonist muscles. Exercises like proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching can enhance reciprocal inhibition and overall muscle coordination.
- Regular Monitoring and Adjustment: Continuously monitor your progress and adjust your training program as needed. Regular assessments will help you identify any new imbalances and address them promptly.
Conclusion
Understanding and addressing muscular imbalances and optimizing reciprocal inhibition are essential for enhancing mobility, preventing injuries, and improving overall physical performance. By incorporating these evidence-based practices into your training routine, you can achieve a balanced and functional musculoskeletal system.
For more detailed information and resources, you can explore the studies and articles cited in this blog.
References:
- Abu Owida, H., De Fazio, R., Al-Naami, B., & Visconti, P. (2023). Electromyography monitoring systems in rehabilitation: A review of clinical applications, wearable devices and signal acquisition methodologies. Electronics, 12(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12071520
- American Council on Exercise. (2019). Joint mobility and stability. Retrieved from American Council on Exercise
- Fazli, M., Sadeghi, H., Mahdavi, M., & Davoudi, A. (2023). Association between physical activity and body posture: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-14216-1
- Jawade, A., Chogle, A., Khan, M. S., Shaikh, S., & Gill, B. (2023). The effect of reciprocal inhibition techniques on pain, range of motion, and functional activities in patients with upper trapezitis. Cureus, 15(2), e34487. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.34487
- Ritzmann, R., Freyler, K., Krause, A., Gollhofer, A., & Donath, L. (2023). Neural mechanisms underlying muscle coordination and reciprocal inhibition during dynamic activities. Frontiers in Neuroscience. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2023.1205602