Efficacy of Acupuncture for Peripheral Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy is a debilitating condition characterized by damage to the peripheral nerves, often leading to pain, tingling, and sensory impairments. This condition is prevalent among individuals with diabetes, chemotherapy patients, and those with other underlying health issues.
This blog will explore the efficacy of acupuncture in treating peripheral neuropathy, focusing on recent evidence from systematic reviews, clinical trials, and case reports.
Clinical Question
"Is acupuncture effective in treating peripheral neuropathy, resulting in a greater reduction in pain and improvement in sensory function?
How certain conditions affect the Peripheral Nervous System(PNS)
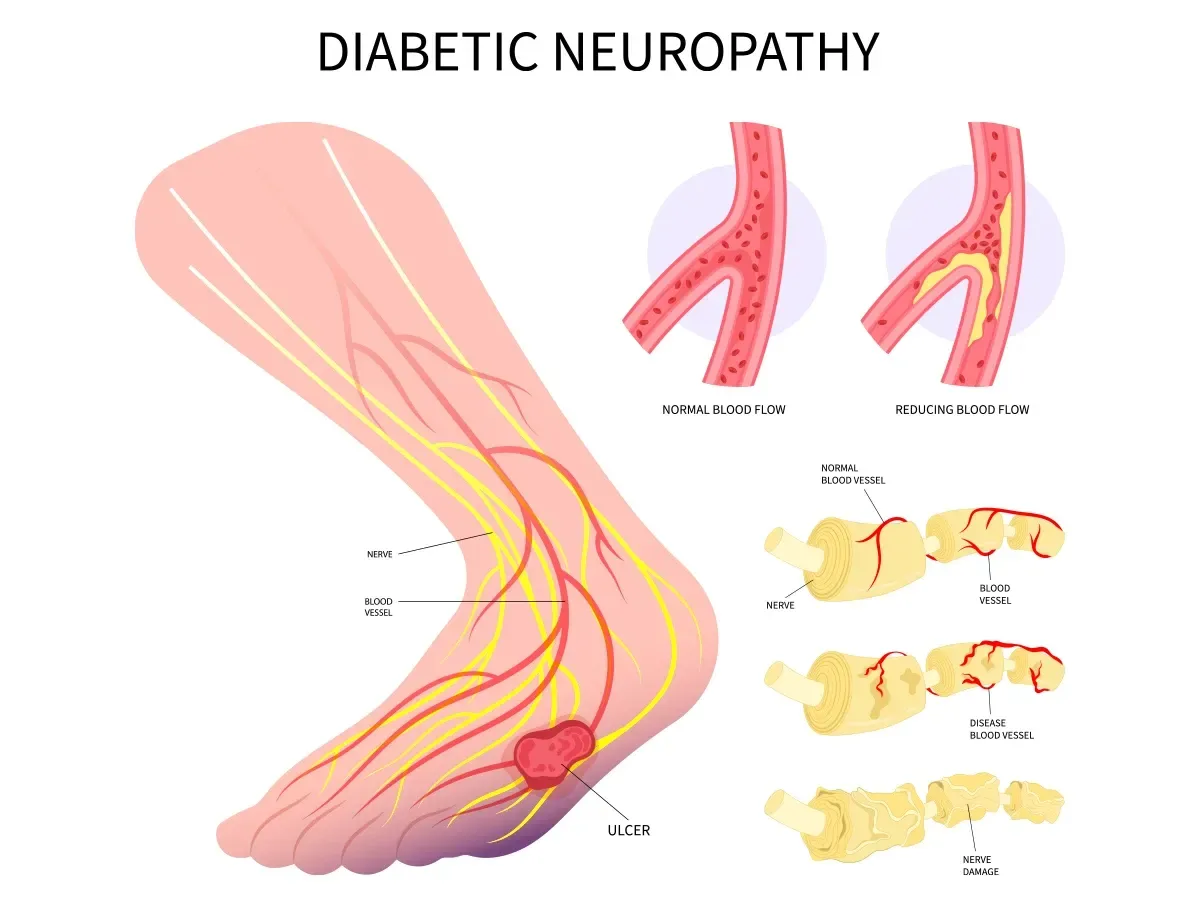
Diabetes, chemotherapy, infections, and trauma affect the peripheral nervous system, which includes all the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. These conditions lead to the deterioration of nerve fibers, impairing their ability to transmit signals effective.
The symptoms can be severe and often include:
- Chronic pain
- Numbness and tingling
- Sensory loss
- Muscle weakness
Overview of conditions:
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage nerves over time, leading to diabetic neuropathy. This damage is often associated with poor blood flow, which deprives nerves of essential nutrients and oxygen, resulting in their degeneration (Callaghan et al., 2012).
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapeutic agents, while targeting cancer cells, can also cause collateral damage to peripheral nerves. This damage often leads to chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy, characterized by pain, numbness, and tingling in the extremities (Flatters et al., 2011).
Infections: Certain infections, such as HIV or Lyme disease, can directly infect nerves or cause inflammation that damages nerve fibers. This inflammatory response can disrupt the normal function of the peripheral nervous system, leading to neuropathic symptoms (Cornblath, 2012).
Trauma: Physical injuries can sever or compress nerves, leading to immediate and sometimes permanent nerve damage. This type of neuropathy can cause severe pain, loss of function, and sensory disturbances in the affected areas (Campbell, 2012).
Acupuncture as an Intervention
Acupuncture, a key component of traditional Chinese medicine, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate nerve function, promote blood flow, and relieve pain. It has been used for centuries to treat various conditions and has gained attention for its potential benefits in managing peripheral neuropathy.
Sampled Point TCM Prescription/Function & Associated Nerves
Points for treating peripheral neuropathy include:
- ST36 (Zusanli): This point is located below the knee on the tibialis anterior muscle. It is associated with the deep peroneal nerve, which plays a role in enhancing immune function and improving blood circulation, critical for promoting nerve health and reducing neuropathic pain.
- SP6 (Sanyinjiao): Found on the inner leg, above the ankle, this point involves the tibial nerve. This point helps in maintaining overall neurological health and function.
- LI4 (Hegu): Situated on the hand between the thumb and index finger, this point is associated with the superficial branch of the radial nerve. It is effective in alleviating pain and boosting the immune response, crucial for managing neuropathic symptoms.
- LV3 (Taichong): Located on the foot between the first and second toes, this point involves the deep peroneal nerve. It regulates liver function and alleviates pain, contributing to improved nerve function and reduced neuropathic discomfort.
- GB34 (Yanglingquan): This point is found on the lateral aspect of the leg, below the knee, and is associated with the common peroneal nerve. It benefits the tendons and alleviates pain, helping restore muscle function and reduce neuropathic symptoms.
- BL60 (Kunlun): Located behind the ankle, in the depression between the Achilles tendon and the ankle bone, this point involves the sural nerve. Known for its analgesic properties, it helps reduce pain and promote relaxation, aiding in the management of peripheral neuropathy.
Reviewing the Evidence
Case Report
Schroeder & Tiran, 2011 detailed the use of acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. The patient, who suffered from significant pain and sensory disturbances, showed remarkable improvement following a series of acupuncture sessions. This case highlights acupuncture's potential to alleviate symptoms of peripheral neuropathy resulting rom chemotherapy, further broadening its applicability.
Clinical Trial
Li et al., 2024 explored a clinical trial of acupuncture's effectiveness for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This study involved a randomized controlled trial comparing acupuncture treatment with standard medical care. The results demonstrated that patients receiving acupuncture experienced a greater reduction in pain and a marked improvement in sensory function compared to those receiving standard care. This trial provides robust evidence supporting acupuncture's role in treating peripheral neuropathy.
Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Xiao et al., 2023 conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis examined the efficacy of acupuncture for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. This comprehensive analysis included numerous studies and concluded that acupuncture significantly reduces pain and improves sensory function in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The findings underscore the potential of acupuncture as a viable treatment option for managing this condition.
Updated Study
Zhang et al., 2024 published in the European Journal of Integrative Medicine examined the long-term effects of acupuncture on patients with peripheral neuropathy. The study found that acupuncture not only provided immediate relief but also contributed to sustained improvements in sensory function and pain management over several months.
Conclusion
The evidence from recent studies and clinical reports strongly suggests that acupuncture is an effective intervention for treating peripheral neuropathy. Patients undergoing acupuncture treatment have reported significant reductions in pain and improvements in sensory function, making it a promising option for those seeking relief from this challenging condition.
References:
- Campbell, W. W. (2012). Evaluation and management of peripheral nerve injury. Clinical Neurophysiology, 123(10), 1951-1965. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2012.06.019
- Cornblath, D. R. (2012). Acute and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy. Continuum: Lifelong Learning in Neurology, 18(1), 39-61. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.CON.0000427552.79763.8e
- Flatters, S. J. L., Dougherty, P. M., & Colvin, L. A. (2011). Clinical and preclinical perspectives on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): A narrative review. British Journal of Anaesthesia, 107(6), 777-787. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aer260
- Li, H., Wang, J., Chen, Y., & Liu, M. (2024). Clinical trial on acupuncture for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Frontiers in Neurology, 15, 1402458. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2024.1402458
- Schroeder, S., & Tiran, D. (2011). Case report on acupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Case Reports in Medicine, 2011, 920807. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/920807
- Xiao, Y., Zeng, Y., Liang, F., & Zhang, X. (2023). Systematic review and meta-analysis on acupuncture for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Frontiers in Neurology, 14, 1281485